Barrier property for plastic flexible packaging
Barrier property is the most important characteristic of packaging materials. In particular, the shelf life of food is highly dependent on the barrier property of packaging materials. The so-called barrier material refers to the standard state (23°C, 65% relative humidity). A 25.4-micron-thick film is a material whose oxygen permeability is below 5ml (㎡.d) and moisture permeability is below 2g/(㎡.d). At present, aluminum foil, EVOH and PVDC belong to the range of high barrier materials in flexible packaging; Nylon and polyester are among the medium barrier materials; plastic films such as PE and PP are low barrier materials.
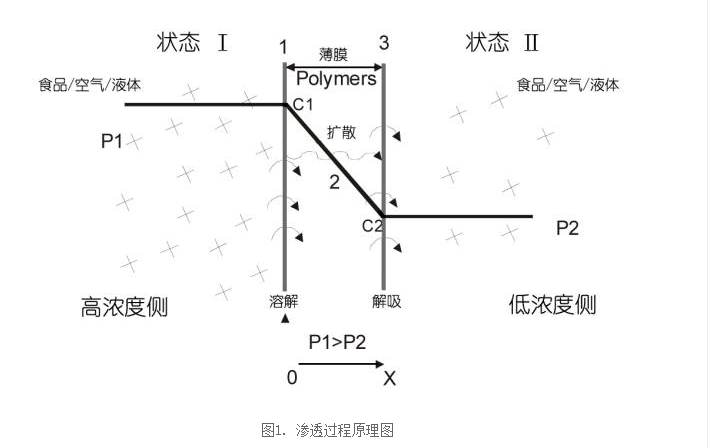
Principle of permeation: Generally, the barrier properties of materials we talk about are for specific permeable objects. Permeable objects include common gases, water vapor, liquids, organics, etc. The material penetrates from one side of the specific permeable object to the other. The barrier performance of the side (usually the high-concentration penetration through the material into the low-concentration test). The entire permeation process can be divided into adsorption, dissolution, diffusion, and desorption. Gas or water vapor enters the surface of the material from the high-concentration area, diffuses inside the material, and desorbs from the other surface of the low-concentration area, as shown in the figure