Knowledge about Food Packaging
1. Overview of Food Packaging
Due to the diversity of food, the complexity of ingredients, and the variability of food quality caused by the circulation environment, the application of Food packaging materials and technology has become very complex. It is very difficult to truly realize the three functions of "protecting products, convenient storage and transportation, and promoting sales". In the face of a wide variety of food and numerous consumption channels, food packaging has become more and more important to help consumers purchase quickly. Making a right food packaging is a growing challenge. Therefore, understanding the principle and characteristics of food packaging is very important to do a good job in food packaging.
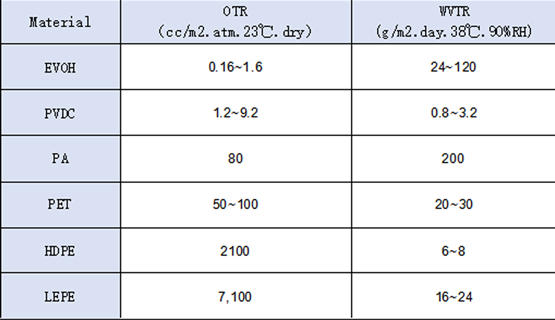
The advantages of Composite film make it the main packaging material for food. According to the characteristics of the packaged food, the conditions of production and packaging equipment, the environment and mode of circulation, the composite film can be optimized with advantages of each layer film, and combine into a diversified composite film through printing, laminating and other flexible packaging production processes, which can just solves the personalized problems encountered in the production and circulation of various different foods. It has good applicability. This is also the reason why the amount of composite film is the largest and significantly larger than the amount of paper, glass, metal and other materials used in food packaging.

2. Food Requirement for Packaging Film
Environment effect on food quality
The food quality is an important index to evaluate whether the packaging composite film is designed properly. In the circulation process, food will be affected by environmental factors such as oxygen, moisture or humidity, temperature and so on. In order to design a suitable structure for packaging film, it is necessary to be clear:
• What effect do these environmental factors, especially oxygen light, moisture or humidity, have on food?
• What structure of composite film can control these environmental factors, so as to avoid the bad effects on food?
Therefore, it is very important to understand the impact of these environmental factors on food quality.
(1) Oxygen Effect on Food Quality
Oxygen in the air is an important factor that causes the change of food quality in the circulation process. The main factors that cause food changes include:
1) Oil Oxidation
A lot of food raw materials contain oil itself, in the food processing process, it may also add oil. In the storage circulation process, these oils will speed up the oxidation after contact with oxygen, produce a sour taste and some toxic compounds, which is called oil rancidity. The oxidation rate of oil will be affected by the oxygen concentration. When the oxygen is very sufficient, the oxygen proportion has no effect on the oxidation reaction speed. However, when the oxygen proportion is low, the oxygen proportion is proportional to the oxidation reaction. So the composite film with high barrier can slow the oil oxidation rate. In addition, with higher temperature and larger surface area of the food, the oil oxidation will be faster, which will have higher barrier requirements of the packaging film.
2) Oxygen effect on color
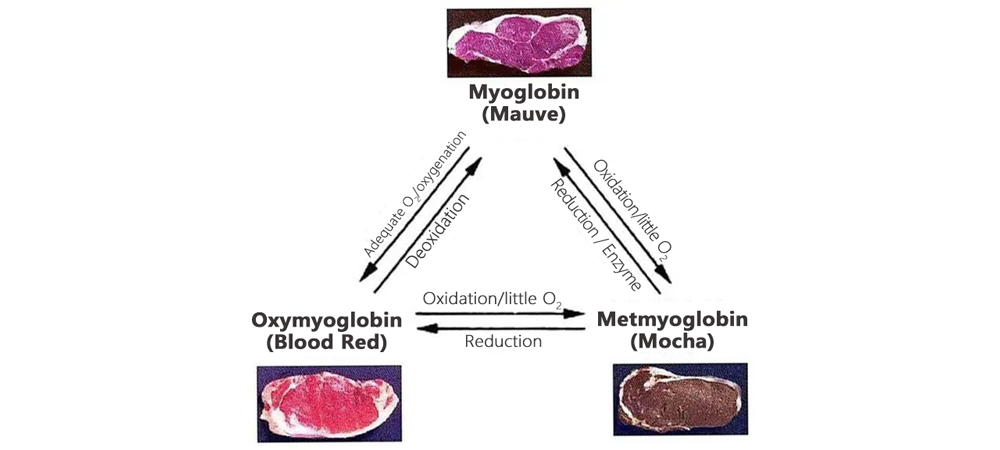
Freshly slaughtered meat is purple red, due to lots of myoglobin; after stored in the air for 30 minutes, myoglobin will be combined with oxygen to generate oxygenated myoglobin, so the meat will turn bright red, which is the characteristics of fresh meat. Myoglobin and oxymyoglobin can be oxidized into Methemoglobin, which causes flesh color turns brown and becomes dark, not conducive to sales. The flesh color changing process may be fast for a few hours, slow for a few days, it is necessary to prevent the entry of oxygen, so as to slow down the process from bright red to brown.
3) Oxygen effect on microorganism
Microorganisms are important factors causing food spoilage. According to the relationship between microorganisms and oxygen, it can be divided into aerobic bacteria, facultative anaerobic bacteria, anaerobic bacteria. Aerobic bacteria need oxygen to grow and reproduce; Facultative anaerobes can grow in either aerobic or anaerobic conditions, but the aerobic condition is better; aerobic bacteria can also grow and reproduce in the absence of oxygen. Food microbial species will vary with food raw materials, production hygiene conditions and sterilization methods. Packaging enterprises should get to know about the microbial species and their sensitivity to oxygen during the circulation of food, so as to carry out the right oxygen resistance design of composite film. The composite film with high oxygen resistance can inhibit the growth and reproduction of aerobic bacteria and facultative anaerobic bacteria, but has little effect on anaerobic microorganisms.
4) Oxygen effect on vitamin
Vitamins are life-sustaining substances. Lack of vitamin A can cause growth retardation, dry eye disease, night blindness and other problems in children. Many foods contain vitamin A or carotenoids that can be converted into vitamin A by animals, such as cod liver oil, dairy products, egg products, animal liver, carrots, sweet potatoes, pea seedlings, cooked spinach, cooked broccoli, green peppers, etc. But chemical nature of vitamin A is lively, easy to be oxidized in the air. Vitamin C in fresh or freshly-cut fruits and vegetables is also easy to be oxidized in the air. Vitamin E is sensitive to oxygen, easy to be oxidized and lose activity, and oil oxidation can also accelerate the destruction of vitamin E; plus, vitamin E in dry food is easier to be oxidized.
5) Oxygen effect on fresh-keeping of fruits and vegetables
Different from processed foods, which has to avoid oxygen exposure, fresh fruits and vegetables need to undergo respiration to maintain normal physiological activities and keep them fresh. And respiration needs to take in oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide, so it requires oxygen inside the package. However, the oxygen proportion of fruit and vegetable packaging should not be too high or too low, since if it's too high, the respiration will be too strong, resulting in the faster maturation and aging, easy to rot; Too low oxygen is prone to anaerobic respiration, which will generate ethanol, faster decay. Therefore, the proportion of oxygen in the package should be the best to maintain the lowest respiration of fruits and vegetables without anaerobic respiration. For most fruits and vegetables, the proportion of oxygen in the package should be maintained at 3%-5%.
The oxygen content in the packaging also has an important impact on the color change of fruits and vegetables. Low oxygen can make mushrooms, strawberries, fresh cut horse bells, fresh cut apples and many other fruits and vegetables maintain good color. High levels of oxygen can also promote redder shades of safflower, orange oranges and darker shades of blood orange, meanwhile, it also inhibit freshly-cut vegetables turning brown.
In addition, the amount of carbon dioxide in the packaging also has different effects on respiration and color change. Some fruits and vegetables are not sensitive to carbon dioxide, but some fruits and vegetables, such as citrus, will turn brown and generate abnormal flavors at very low carbon dioxide concentrations. Therefore, for fruits and vegetables, including freshly-cut fruits and vegetables and those packed in MAP (Modified Atmosphere Packaging) , choosing the right packaging film with suitable gas resistance (including oxygen and carbon dioxide resistance) has an important impact on fruit and vegetable protection
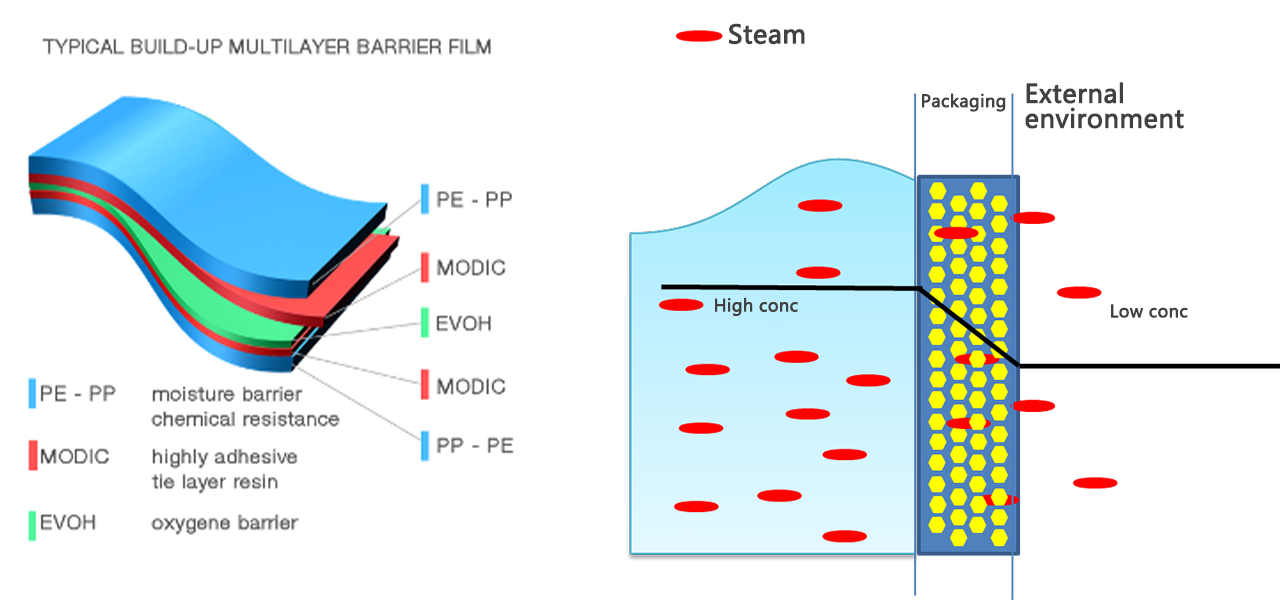
(2) Moisture Effect on Food Quality
The humidity in the environment will affect the water content of food, such as with low humidity, food may lose water; with high humidity, food may be damp. However, the food quality is not directly related to the water content, but to the "available water" in the food, so a concept called water activity (Aw) was proposed. Water activity (Aw) is the ratio of water vapor at equilibrium in a closed container to the saturated vapor pressure of pure water at the same temperature. Water activity is a better indicator than water content in judging spoilage of food. Under normal circumstances, food producer can provide food water activity value, of course, packaging enterprises can also use water activity meter and other equipment for testing.
1) Moisture effect on oil oxidation
In foods with very low water activity (Aw< 0.1), fat oxidation is rapid. With the increase of water activity, the oxidation rate decreases, and when Aw increases to about 0.25, the oxidation rate becomes minimum, and as the water activity continues to increase (Aw between 0.25 and 0.8), the oxidation reaction is accelerated. However, when the water activity was too high (Aw between 0.8 and 0.99), the added water slowed down the oxidation of the fat.
2) Moisture effect on microorganism
The growth and reproduction of microorganisms in food need water to carry out, and there is a minimum requirement for water activity. In general, bacterial Aw>0.94, mold Aw>0.80, yeast Aw>0.87, but when Aw<0.6, the vast majority of microorganisms fail to grow.
3) Moisture effect on food properties and flavor
Dry food is sensitive to humidity, and it is easy to absorb moisture when the humidity is high. For example, the water content of freshly processed tea is about 3% under the environment of relative humidity of 20%RH. However, at 50%RH, tea will absorb moisture and the water content will increase to 5.5%. Plus, the water content can reach 13% at 80%RH. When the water content of tea exceeds 5.5%, its organization state, flavor, color and nutritional value will decline sharply, which seriously affects the quality of tea. For food with high water content, when the humidity is low, it is easy to lose water, harden or deform, causing changes in hardness, chewiness and elasticity.
4) Moisture effect on fruits & vegetables
Fruit and vegetable have lots of water, however, even in a high humidity environment they will also lose water, resulting in surface shrinkage, bad taste, or turning wood fibrosis. If there is too much water loss, condensed water is easy to appear in the package, resulting in the growth of microorganisms and causing the deterioration of fruits and vegetables.
(3) Effect of Light on Food Quality
1) Effect of light on oil oxidation
Besides oxygen, light can also accelerate oil oxidation. Especially some foods contain some natural pigments such as chlorophyll hemoglobin, which is a photosensifier and will cause photosensitized oxidation. The oxidation rate with light effect is over 1000~1500 times faster than that without light. Chlorophyll is a kind of lipid-containing pigment family. For some food containing green plant raw materials, chlorophyll contained in it will be affected by light and oxygen, and will be photolysis into a series of small molecular substances and fade in the processing and storage process. In meat and poultry, due to the blood is not put clean when slaughtered, the meat still contains hemoglobin, and it is easy to occur photooxidation.
2) Effect of light on vitamin
Light will cause the loss of some photosensitive vitamins. Vitamin B, which is a photosensitizer, wil see light decomposition to produce photoflavin; And photoflavin is a strong oxidant, easy to cause nutritional value reduction and bad odor in milk products, so milk products should be packed away from light.
Vitamin D, which is widely found in animal foods, is not easily oxidized, but it can cause fat oxidation reaction due to ultraviolet radiation. For example, the content of vitamin D in fish oil with ordinary packaging decreases continuously during storage and is almost lost after 4 weeks. Vitamin E is sensitive to both oxygen and ultraviolet light, easy to accelerate oxidation after ultraviolet radiation. Vitamins A, B6, B12, and K will be destroyed by UV exposure.