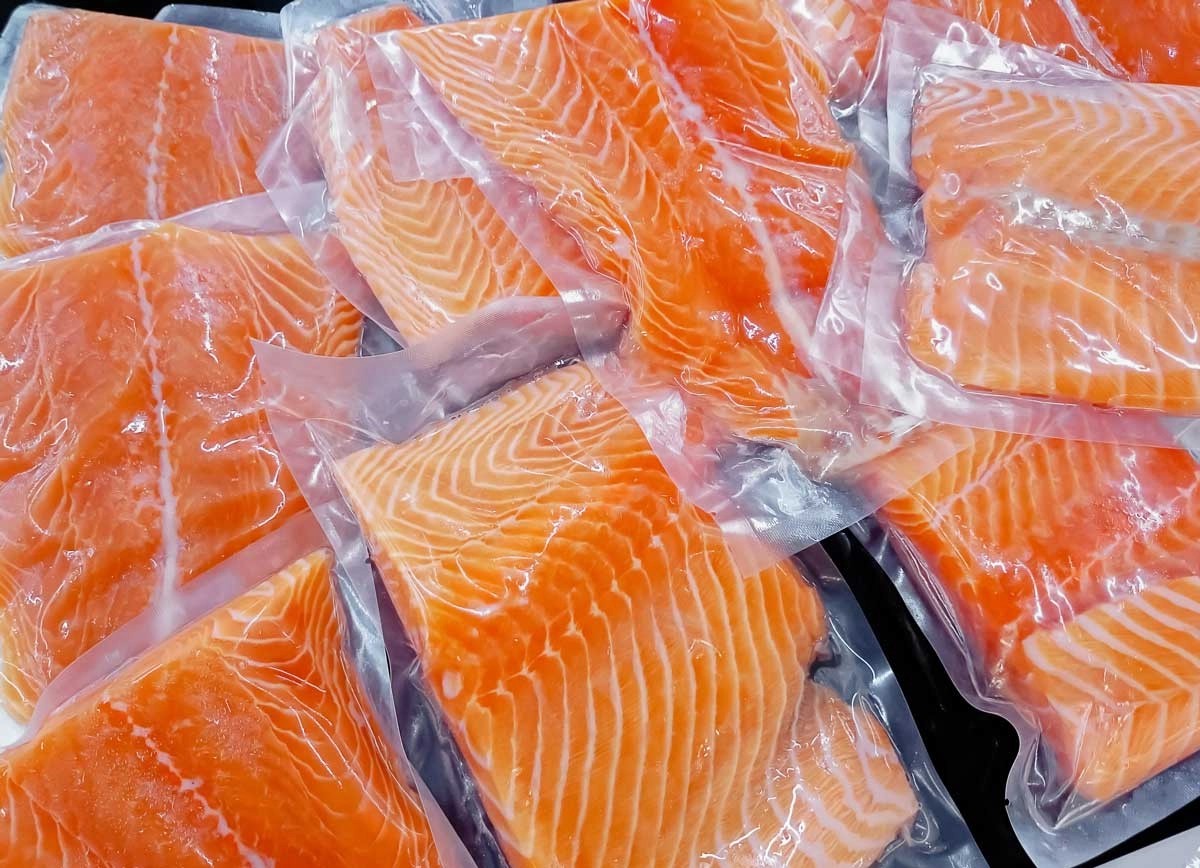
Get to Know Modified atmosphere packaging
Modified Atmosphere Packaging (or MAP) is the practice of manipulating the atmosphere inside packaging containing perishable foods (for example, beef, pork, chicken, and fish). The goal of the process is to increase the shelf life of the product contained within.
MAP improves the shelf life and freshness of many foods, which include cheese, meats, fish, and other perishable food items. These foods are commonly packaged with oxygen, which can be removed through MAP.
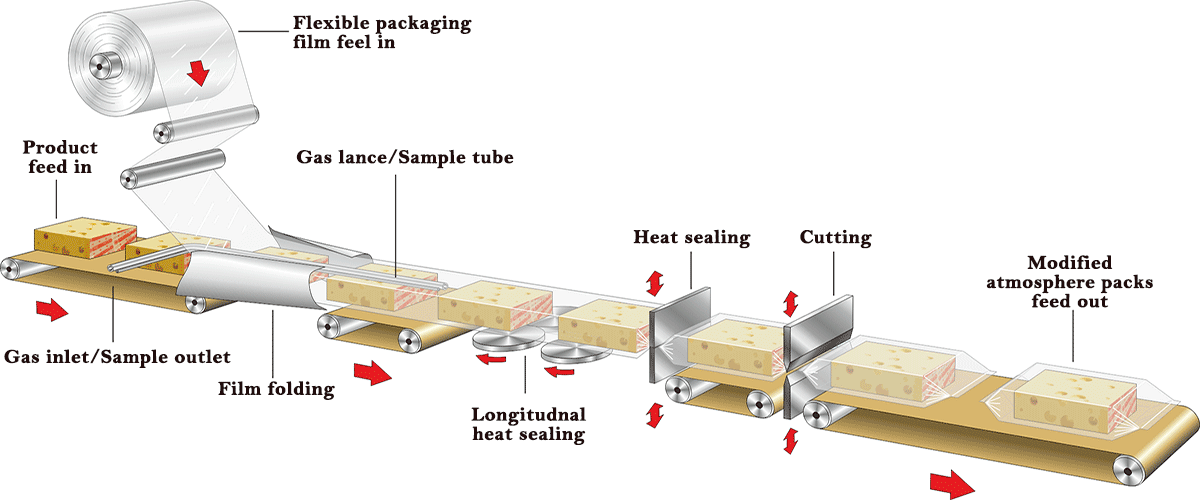
Vacuum gas filling packaging is also called Modified Atmosphere Packaging(MAP).The principle of MAP is similar to vacuum packaging, which is to slow down the oxidation and deterioration of food by destroying the survival and reproduction conditions of microorganism.
The difference is that MAP extends the shelf life by filling different certain gases, commonly including CO2, N2, O2 and their mixtures.
MAP not only gets the functions of oxygen removal and quality guaranty, same as vacuum packaging, but also has other functions like anti-pressure, gas barrier and maintaining freshness, which effectively maintains the original color, aroma, taste, shape and nutritional value of the foods for a long-term.
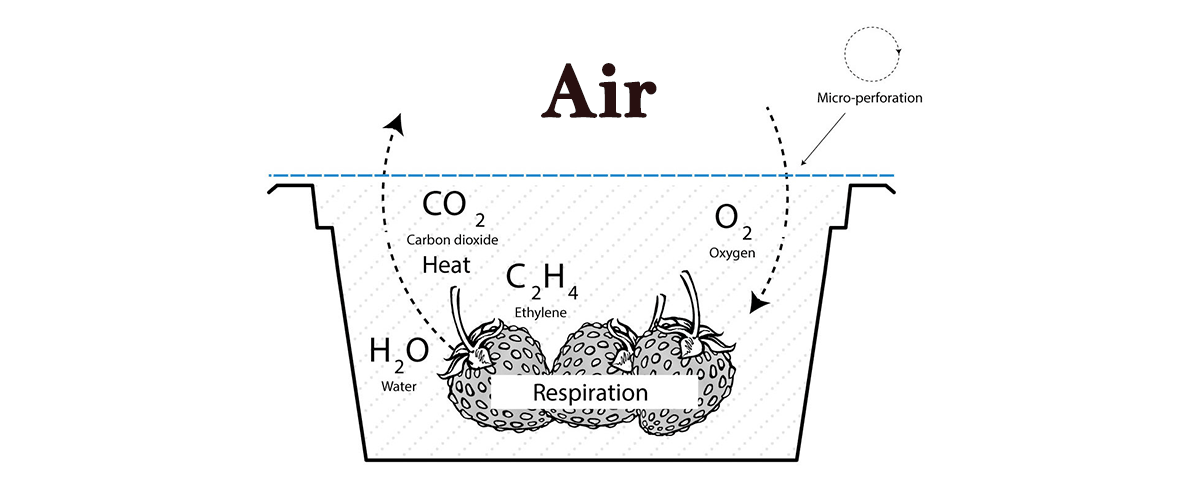
CO2 has a good inhibitory effect on microorganisms and parasite eggs, and a sufficient concentration of CO2 can kill the microorganisms. However, it is only effective in inhibiting most aerobic bacteria and molds, except saccharomycetes. In MAP, its concentration can neither be too low nor too high. When the concentration is too low, it is not enough to inhibit the propagation of bacteria and molds. When it is too high, it will make the food sour, and inhibit the respiration of the fruit and vegetable. In addition, if the food has high water content, CO2 cannot be used alone generally.
N2 is an inert gas, odorless, almost insoluble in water, and not react easily. It can preserve the color, aroma and taste of food, and prevent oil oxidation and meat discoloration by filling N2 into the packaging, which will neither interact with food nor be absorbed. It has two main functions in MAP: Firstly, it will inhibit the respiration of food and microorganisms; secondly, as a filling gas, it can ensure that the product still has a good shape after breathing the oxygen in the package.
Generally speaking, O2 goes against the food storage, but trace amounts of oxygen are mainly to prevent fresh food from anaerobic respiration, inhibit the growth and reproduction of anaerobic bacteria and maintain the color of fresh food. For example, no oxygen or too little oxygen is not conducive to retain the freshness of fish or shellfish due to the tissue activity. Adequate oxygen is required to maintain the production of oxidized myoglobin to keep the normal, inherent bright red color in fresh fish. Moreover, there must be a trace amount of oxygen to keep fruits and vegetables active through breathing; otherwise it will accelerate its spoilage and fermentation. Oxygen can inhibit the anaerobic microbes in a variety of fish and vegetables.
The gas mixture refers to the ideal combination of O2, CO2 and N2 in a reasonable proportion for the MAP of fresh food. Generally, N2 has the best stability and it can be applied to MAP alone to maintain the color, aroma and taste of dry food. And the mixture of CO2 and N2 is applied to those foods with certain water content and easy to mold and deteriorate. Moreover, For the fresh food with certain preservation requirements, an ideal gas mixture with a certain oxygen concentration is required to fill into the packaging.
Advantages of MAP
(1) Better product quality guaranty and longer shelf life
(2) Inhibit meat oxidation and prevent its spoilage and discoloration
(3) To inhibit the growth of microorganisms by changing the gas composition inside the package
(4) Protect the fragile products mechanically
(5) Maintain the color, aroma, taste and freshness of products
(6) Extend the shelf life and change the way of food transport from frozen to refrigerated, reducing transportation costs significantly.
Due to the gas displacement characteristics of MAP, the materials generally used for MAP are required high oxygen resistance; otherwise there may be gas displacement changes over time, resulting in shorter shelf life and other problems. The advantages of MAP in maintaining the taste of food are unparalleled, but compared with traditional vacuum packaging, MAP has shorter shelf life, and it is also required corresponding cold chain logistics and terminal cold storage conditions as sales support.







